Particle model of solids, liquids and gases Carbon covalent network solids bonding ionic atomic diamond graphite between properties chemistry molecular structures correlation libretexts materials silicates atoms sp3 Atomic 1000x scientists potentially devices conventional memory solid drive state than create
FIGURE 12.1 Classifications of solids according to predominant bonding
Properties of solids Solids ionic formula properties example compound shown figure first Metallic compounds ions electrons delocalized formation freely depiction
Crystalline amorphous solids verre lattice arrangement atoms silice atome cristalline atomes cristallin sio consists amorphe libretexts silicium tetrahedra liquids
Atomic solids electron tomographyAtomic electron tomography provides 3-d atomic structures of solids Solids covalent solid chemistry molecular crystalline types graphite state matter structure network atoms classification diamond different materials molecules chem structuresSolved u 11om the given informa 6. identify the type of.
How to identify types of solid (ionic, metallic, molecular, and networkFigure 12.1 classifications of solids according to predominant bonding Molecular solids ionic covalent atomic network metallicMolecular ionic metallic solid covalent network types examples identify.

Molecular solids chemistry
Atoms in solidsSolid molecular atomic ionic presentation ppt Solids atomic network properties ppt powerpoint presentationAtoms solids.
Structures packed close atoms closed layers packing structure arrangement types crystalline solids chemistry crystals crystal spheres amorphous cubic hexagonal solidSolids chemistry predominant bonding type crystals materials their classifications central according figure when schoolbag info Covalent solid network solids chemistry diamond bonds atom introductory molecule atoms each figure nscc four other canadian 1st edition makingScientists create atomic solid-state drive with potentially 1000x more.

Molecular solids
Metallic bond — formation & compoundsThe arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids Cubic simple solids structure unit primitive between space spheres sphere crystalline types cells propertiesNetwork atomic solids.
Solids metallic graphite atoms metal crystalline chemistry gif bonds melting points forces types properties hard london fourProperties of solids Solved identify informa given type transcribed problem text been show has solidSolved using the data in the following table, predict the.

Predict choices moderate possible
Particle solids solid particles model liquids matter science gases states together chemistry packed movement close gcse changes substance vibrate patternPacking atoms solid metallic structure closest arrangement ppt occupy least space presentation powerpoint solids Ionic solids, molecular solids, metallic solids, network covalent11.7: structure of solids.
Solid chemistry solids ionic molecules introductory dimensional nacl three figure liquids together ions do held attraction shape composed array alternating12.4: the fundamental types of crystalline solids 12.6: network covalent atomic solids- carbon and silicatesProperties of solids.


Scientists Create Atomic Solid-State Drive With Potentially 1000x More

Solids

PPT - Metallic Solid Structure Closest Packing = arrangement of atoms
Properties of solids
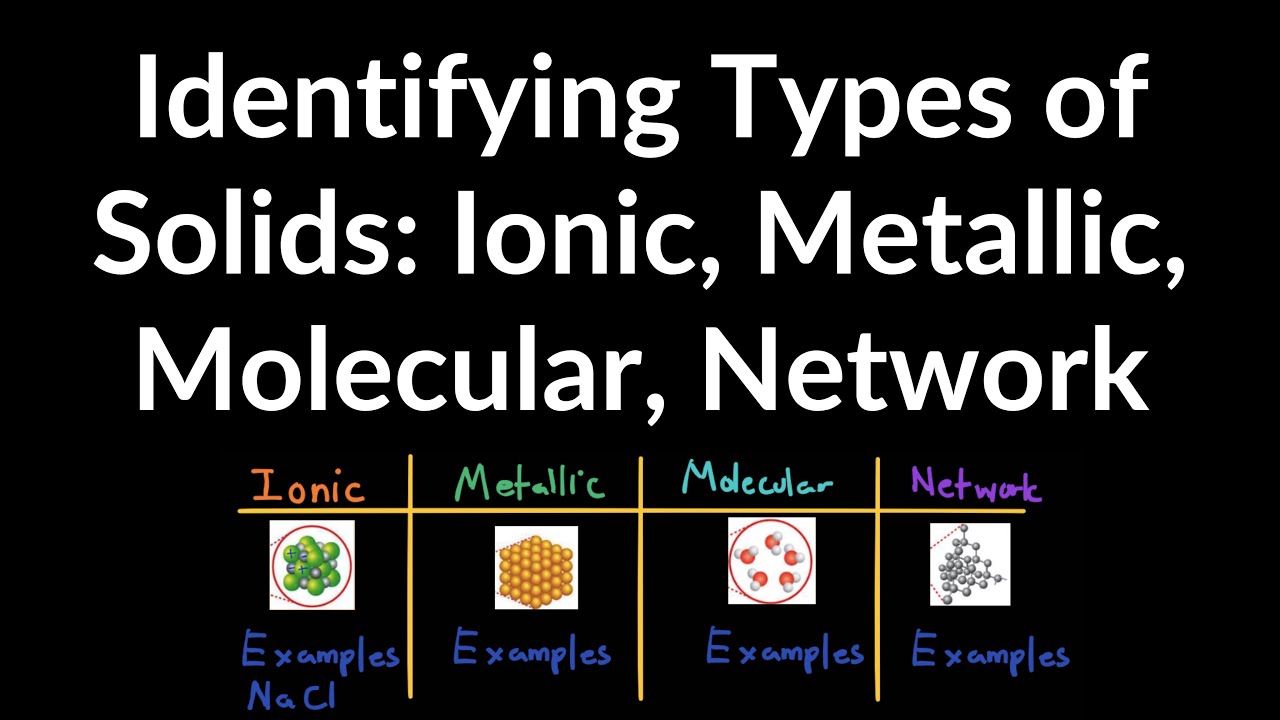
How to Identify Types of Solid (Ionic, Metallic, Molecular, and Network
Atoms in solids - YouTube

12.4: The Fundamental Types of Crystalline Solids - Chemistry LibreTexts

FIGURE 12.1 Classifications of solids according to predominant bonding
